Interested in imaging with far-red fluorescent probes? Expand your multiplex capabilities with near-infrared (NIR) modules for the FV3000 microscope, including a 730 nm or 785 nm diode laser and GaAs PMTs for high-sensitivity detection up to 890 nm.
- Greater multiplexing capabilities
- Reduced autofluorescence
- Gentler live-cell imaging
- Deeper imaging with less absorption and scattering

Related Videos
NIR Laser Diodes
|
| Applicable dyes for NIR imaging
|
| Cooled GaAs PMT Detector for NIR Imaging
|
|---|
High Transmittance Optics for NIR Imaging
High transmittance from VIS to IR with silver-coated scan mirrors and Olympus’ unique 1600 Coating on the scan lens.
|
|
Deep Tissue Observation with Silicone Oil Immersion Objectives in the NIR
- NIR fluorescence works well for deep imaging because NIR light scatters less in live tissue
- The refractive index of silicone oil (ne≈1.40) is close to that of living tissue (ne≈1.38), enabling high-resolution observations deep inside living tissue with minimal spherical aberration
- The UPLSAPO30XIR (NA 1.05, WD 800 μm) offers higher NIR transmittance thanks to Olympus’ 1600 Coating
|
|
Multiplexing with X Line High-Performance Objectives
- Greater multiplexing imaging is possible using additional NIR detection channels
- Reduced chromatic aberration during co-localization analysis (corrected at 400 nm–1000 nm)
- Higher numerical aperture, excellent image flatness, and high transmittance from UV to NIR
|
|
TruFocus Red Z-Drift Compensator
| Related Videos |

On-Demand Webinar
 | This webinar will focus on fluorescence multiplexing and deep tissue imaging using near infrared (NIR) laser light. NIR laser sources can help in visualizing biological structures more clearly and at higher resolution deep within the specimen. NIR excitation can also enable the use of more fluorescent dyes without spectral overlap. |
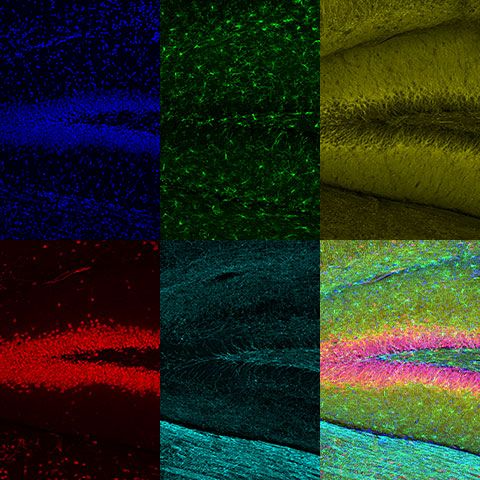
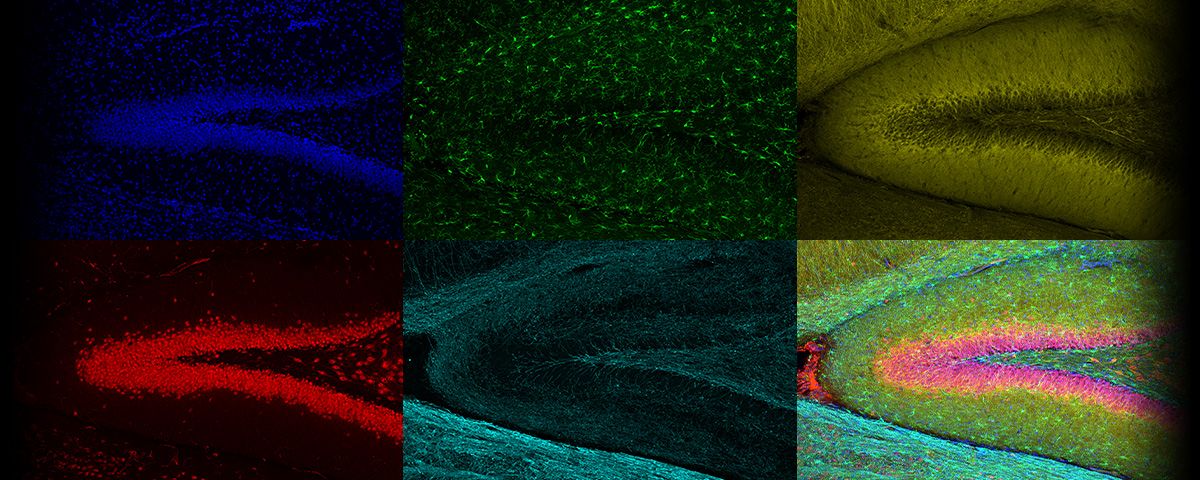
*Banner image: Rat brain slice labeled with Hoechst (blue), anti-IBA1 (Alexa Fluor 488; green), anti-MAP2 (Alexa Fluor 594, yellow), anti-FOX3/NeuN (Alexa Fluor 647; red), and anti-MBP (Alexa Fluor 750; cyan). Images were acquired using a UPLXAPO10X objective with 405 nm, 488 nm, 561 nm, and 730 nm laser lines on GaAsP and GaAs detectors. Maximum intensity projection in Z with TruSight deconvolution processing. Sample courtesy of EnCor Biotechnology. *Product not available in all areas. Contact your local Olympus representative for more information. |
Sorry, this page is not
available in your country.
Sorry, this page is not
available in your country.