Neuroscience and Multiphoton ImagingNeuroscience is the study of nerve function, structure, and development, which involves observing single cells as well as the entire brain—both on the surface and deep within the tissue. If you’re working in neuroscience, you might also need to capture morphological changes and stimulus responses in living samples, but in vivo imaging deep inside the brain is optically challenging. To meet this challenge, we have engineered a complete line up of multiphoton excitation (MPE) A Line objective lenses that enable deep imaging under various conditions. |
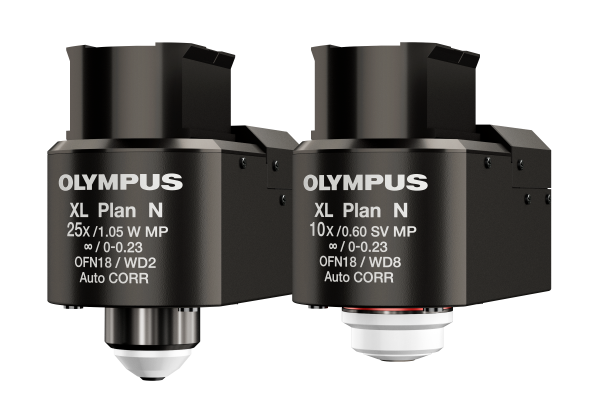
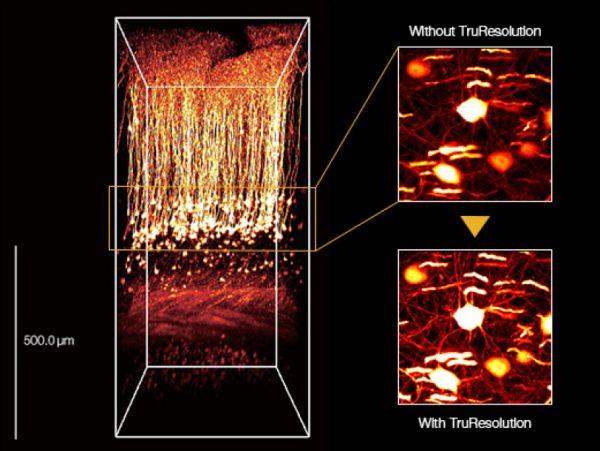
Olympus TruResolution ObjectivesIn the past, compensating for spherical aberration has traditionally required manual correction collar adjustments, which are difficult to make without shifting the focus location and cannot be done along an entire Z stack. Our new TruResolution objectives automatically compensate for spherical aberration thanks to a clever algorithm that finds the best collar setting at each depth using a motorized correction collar. And while spherical aberration usually increases when imaging deeper into the samples, TruResolution objectives maintain optimal compensation as the depth changes. Movement of the collar is automatically coordinated with the microscope focus motor, adjusting the objective Z-position to maintain a consistent focal plane even when the correction collar is rotated. The result is trouble-free, consistently bright and high-resolution images at every depth. |
Deepen the DetailsDeep, in vivo multiphoton brain imaging and optogenetics at high resolution require objectives with high transmission of infrared (IR) light, a high numerical aperture (NA), and the ability to correct for the depth and scattering of tissue. Olympus’ dedicated MPE objectives deliver ultra-broad IR transmission, enabling optogenetic stimulation with visible light down to 400 nm and IR imaging or stimulation up to 1600 nm. The correction collar reduces the excitation volume, enabling stimulation of single cells or dendritic spines. With Olympus TruResolution objectives, the motorized correction collar even offers automated spherical aberration compensation to increase brightness and resolution, revealing fine details at every plane within a deep image stack. Image data courtesy of Katsuya Ozawa and Hajime Hirase, Neuron–Glia Circuitry, RIKEN Brain Science Institute, Japan |
Form with ID "F1" could not be found! |  |
对不起,此内容在您的国家不适用。
对不起,此内容在您的国家不适用。